这里记录PathMatcher的设计以备忘。
首先我们需要知道的是这个PathMatcher的目标是什么。
目标
PathMatcher是LinkCat的注解模块中比较重要的一个匹配器,他是对资源来源注解 resource.origin 功能和结构进行特化的匹配器。所有对于resource.origin注解的匹配都会在这个匹配器里进行。
而这里定义一下resource.origin的值形式:
resource.origin=https/com/github/www/Exfluex/LinkCat
上面是一个非常简单的例子,这里其实可以看到是一个 https://www.github.com/Exfluex/LinkCat 的变体。这里没有用常规的URL形式,而是使用了一种将域名以“.”分段reverse后再构成路径的方式组成。这样的变形有很多好处,第一个好处是便于路径组织,第二个好处是便于正则匹配同时可以用KoaRouter内部使用的path-regex直接操作(舒服)。
这里我们引入一下域名方面的知识,也就是DNS服务相关的一些知识。
首先一个域名是由一些“.”Dot分割开来的域组合而成,比如 blog.oyxf.top 实际上就是三个域构成,而在长期的的网络使用环境下不难发现域名实际从右到左是一个narrow的一个过程。如果用地址来比喻,就是 市.省份.国家 这样的构成。而这里关于DNS解析方面的知识我们引用一下《网络是怎样连接的》一书对于DNS解析的图文(我的实体书忘了放在哪里了,只有先用电纸书截图代替):
下图中是对于DNS解析过程的一个模拟,这里可以明显看到是在执行对 lab.glasscom.com的解析。我们只考虑图片展示的内容的可以得出计算机解析时会找到最近的DNS服务器,而DNS服务器实际先会读缓存,如果命中记录就返回,没有命中就请求上级DNS服务器。而接下来的流程请参考往下第二张图。


这里可以看到实际上DNS解析的过程也是从顶级域名往前进行解析的,我们这里只是将符合人类阅读的格式变为了计算机的实际执行格式。
所以我们将resource.origin注解的值组织形式总结一下就是:
resource.origin = 协议/[顶级域名/主域名/次级域名/..........]/[资源路径]
有了以上的知识,下面我们就开始正式介绍PathMatcher的实现。
可行性
我其实一开始就打算把resource.origin的组织形式改成上面这种格式,因为在我之前使用Koajs时,我就发现Koa-Router内部使用的是path-to-regex来生成对于路径的正则表达式。因此我后面在写linkcat resource.origin相关的matcher时第一时间就想到了上面这种办法。

这里就解决了PathMatcher最大的一个问题,其他的都是一些小细节了。
API层面的使用
这里我们介绍一下怎么在LinkCat插件编写时使用这个PathMatcher的特性。下面以@linkcat/plugin-linkcat-github为例:
GithubPlugin插件

这里可以看到onPag中的ScopeString内就有一个关于resource.origin的限定:
resource.origin=https/com/github/www/:AccountOrProject/:Repository
首先,我们将这个路径匹配字符串成为匹配路径,而这里的 :AccountOrProject 和 :Repository 实际是两个具名参数,因此我们这个匹配路径实际是一个带参匹配路径。
这里其实很好理解,就是把常规的 https://www.github.com/Exfluex/LinkCat URL匹配上,同时把参数 AccountOrProject=Exfluex而Repository=LinkCat。
由于我们这里有两个具名参数,而LinkCat会在匹配时自动将具名参数存储到payload上插件域下的变量列表中,而在插件域下的preparer、filler、finalizer都可以通过payload上指向当前插件数据的current属性拿到这个参数列表。因此这里payload.current[“resource.orign”][“Respository”](注意这里是CaseSensitive的)实际拿到了我们对应的 Repository=LinkCat的值。
MetaRetriever插件
然后我们再来看看metaretriever插件中的带参匹配路径:
resource.origin=:protocol(http|https)/:rest(.*)
这里可以看到有一个具名参数叫protocol,而他的值只有http或者https两种,剩下的被填入rest参数中。
具体一些更加复杂的用法可以参考path-to-regex的文档,但常规情况下这种简单的带参匹配机制就已经比较实用了。
PathMatcher实现
这里先贴一下PathMatcher
export class PathMatcher implements DefaultMatcherProto<PathMatcherConfig>{
matchFn:MatchFunction;
match(target:string){
const res = this.matchFn(target);//很简单的一个内部逻辑,直接匹配字符串
if(res == false)
return null;
return res.params;//将匹配成功时匹配出来的参数传递回去
};
constructor(public id:number,public config:PathMatcherConfig){
this.matchFn = match(this.config.goal);//这里的match函数是path-to-regex提供的用于转换path为正则匹配函数的api函数。
}
}
在开始看PathMatcherFactory代码之前,我们先思考一个问题,上面这种匹配路径的格式能够给我们带来一些什么样的优化呢?首先是可以分段,将前面几段路径做成一个树形结构,比如根节点是 根域(DNS专业名称实际是个Dot)即为空,第二层是https/http/file/smb等协议的域,第三层是顶级域名比如com、org、top的域。然后第四层就是主域名例如github/google/baidu的域,而第五层是叶子节点也是所有被注册的PathMatcher所存在的地方。
但在实际代码实现中我们没有对协议进行匹配,而是直接从顶级域名开始匹配(后面考虑增加IP匹配方法):


简单画个图:

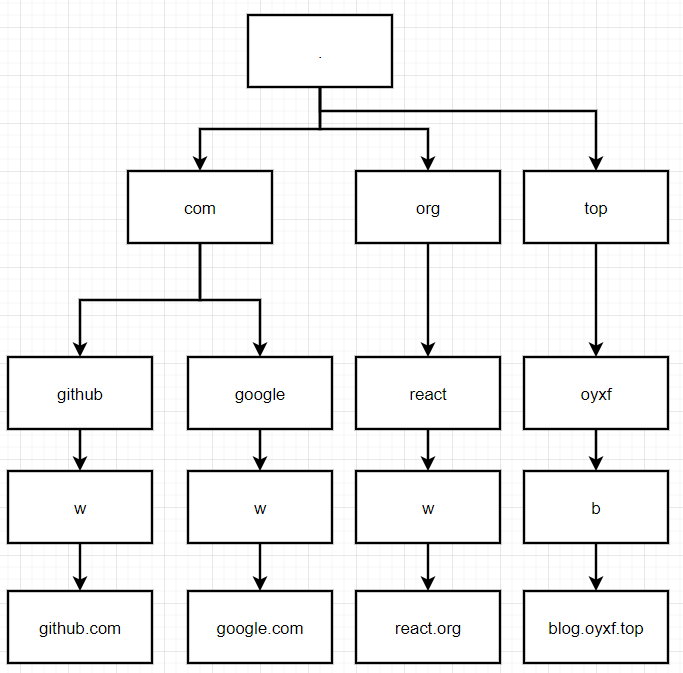
这里就比较明显了首先根节点是根域(第一层),第二层是顶级域名,第三层是主域名,第四层是次级域名的首字母,然后第五层下挂载这叶子节点,也就是我们实际的Matcher在的位置。
我们先看看树结构的实现,是一个比较简单的树节点定义,其中需要注意的是这里面我使用了Symbol定义了一个flag位,判断是否是叶子节点(emm为了后面的拓展设计的,后面准备改成bits flag)。
export namespace PathMatcherFactory{
export type Config = DefaultMatcherProto.Config
export const leaf = Symbol("leaf");
export const index = Symbol("index");
export const pathMatcher = /\/([^\/]+)\/([^\/]+)\/([^\/]{1})/;
export class Node{
[leaf]=false;
}
export class QuickSearchBranch extends Node{
[key:string]:Node;
}
export class QuickSearchLeaf extends Node{
[leaf] = true;
constructor(public matchers:PathMatcher[]=[]){
super();
}
}
}
下面是整个PathMatcherFactory的实现
export class PathMatcherFactory implements DefaultMatcherFactory<PathMatcher,PathMatcherConfig>{
root:PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch=new PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch();//快查树根节点
prior:PathMatcher[]=[];//高优先级或不是path-to-regex类型的的PathMatcher
constructor(public id:number,public config:DefaultMatcherProto.Config){
}
gen(config: PathMatcherConfig): PathMatcher {//生成PathMatcher
const matcher = new PathMatcher(this.generateId(),config);
this.register(matcher);//注册到树上
return matcher;
}
private maxId=0;
private generateId():number{
return this.maxId++;
}
_callback:MatcherCallback=defaultCallback;//细节看之前RenderModule的文章
async match(target: string, env:MatcherEnv): Promise<number> {//匹配入口
let num =0;
this.prior.forEach(async matcher=>{//先把高优先级的matcher执行一遍
const res = matcher.match(target);
if(res != null){
num++;
env.data = res;
const cb = matcher.config.callback??this._callback;
cb(matcher,env);//回调函数
}
});
const res = PathMatcherFactory.pathMatcher.exec(target);//分段path
if(res == null){
//TODO Throw Warnning
return -1;
};
let branch:PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;
branch =this.root[res[1]] as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;//拿到顶级域名 com\org\top节点
if(!branch){
return num;
}
branch = branch[res[2]] as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;//拿到主域名 github/google/oyxf节点
if(!branch){
return num;
}
const leaf = branch[res[3]] as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchLeaf;//拿到次级域名首字母索引节点
if(!leaf){
return num;
}
leaf.matchers.forEach(matcher =>{//执行挂载的Matcher
const res = matcher.match(target);
if(res != null){
num++;
env.data = res;
const cb = matcher.config.callback??this._callback;
cb(matcher,env);
}
});
return num;
}
register(matcher: PathMatcher): this {
if(matcher.config.priority > 0){
this.prior.push(matcher);//如果优先级比较高,就push到prior
return this;
}
const res = PathMatcherFactory.pathMatcher.exec(matcher.config.goal);
if(res == null){
//TODO Throw Warnning
this.prior.push(matcher);//如果无法分段,就push到prior,这里还有bug需要Fix
return this
};
let branch:PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;
let leaf:PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchLeaf;
this.root[res[1]] = branch = (this.root[res[1]]??new PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch()) as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;//构建顶级域名节点
branch[res[2]] = branch = (branch[res[2]]??new PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch()) as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchBranch;//构建主域名节点
branch[res[3]] = leaf = (branch[res[3]]??new PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchLeaf()) as PathMatcherFactory.QuickSearchLeaf;//构建次级域名索引节点
leaf.matchers.push(matcher);//把Matcher存入叶子节点
return this;
}
unregister(id: number): this {//nope
return this;
}
traverse(traverse: Registry.traverseFn<PathMatcher>): this {
return this;//nope
}
find(id: number): Registry.Item<number>[] {
return [];//nope
}
}
这里就是介绍完了PathMatcher的设计和实现中比较核心的内容。
v0.1 wep 完成文章内容编写 2022/03/06